Predictive Maintenance: A company’s hostile service and financial repercussions can be enormous if a machine fails. For this reason. More and more companies are betting on predictive maintenance, a series of actions and techniques applied to anticipate errors. Next, we explain in detail what it consists of and what its main advantages are.
19th-century steam locomotives required constant maintenance. Manual lubrication—operators had to walk through moving parts every few miles and spot which ones need oil—was essential to keep them from overheating. The machinery used in transport today is more sophisticated. However, maintenance is still necessary to avoid breakdowns, and, as in the old locomotives, it is more profitable to detect failures in advance. Predictive maintenance helps to carry out this task.
Table of Contents
What Is Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance is a technique that uses data analysis tools and techniques to detect abnormalities in operation and possible defects in equipment and processes so that they can be solve before failure occurs. Just as predictive analytics makes it possible to anticipate, for example, market movements or fluctuations in energy demand, predictive maintenance uses data analytics to predict system failures and is a fundamental part of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
How Predictive Maintenance Works
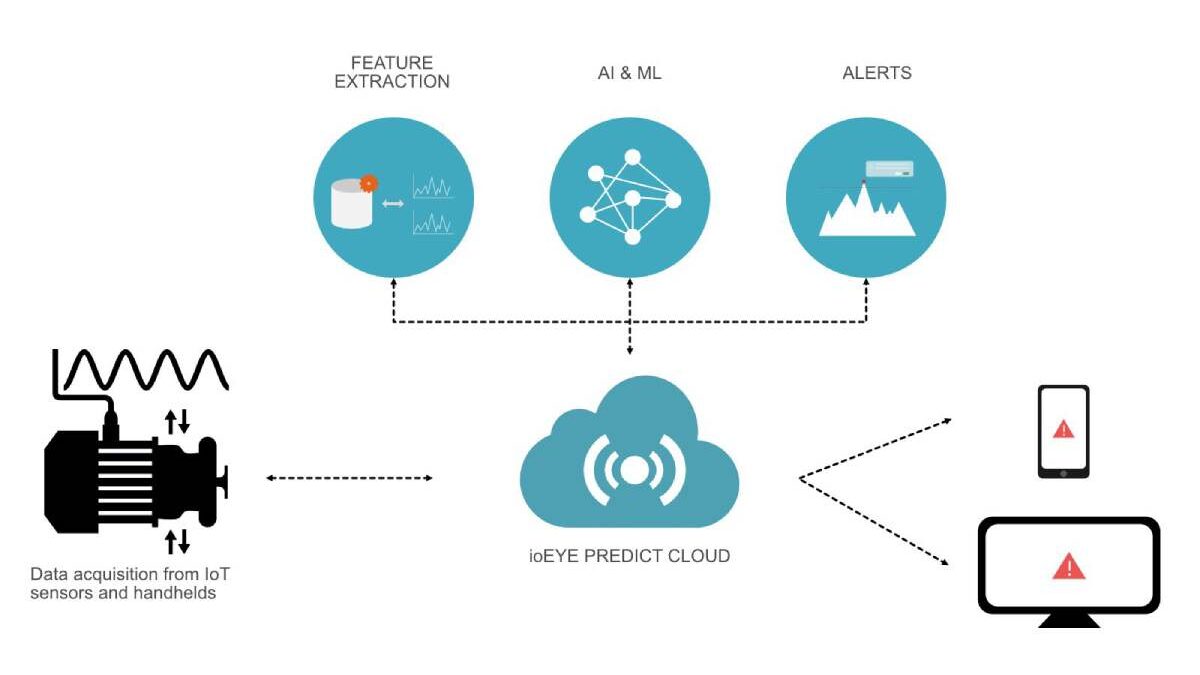
To track the status of equipment and notify technicians of upcoming failures, preventive maintenance has three main components:
- Sensors and connected devices installed on the machines send data on the state and performance of the machine in real-time, thanks to the Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, which allow communication between devices and analysis systems.
- Software solutions and cloud storage ( cloud computing ) enable it to apply data mining and collect and analyze vast amounts of data using big data applications.
- Predictive models are fed with processed data and use machine learning technologies to establish patterns and comparisons, predict failures and schedule maintenance before they occur.
Predictive, Preventive And Corrective Maintenance: Differences
Predictive maintenance is different from preventive and corrective. Despite this, they can all be use simultaneously in the industry. Next, we review their differences:
- Preventive: consists of inspecting the machinery from time to time, regardless of whether it is required or not. Or doing it when a symptom is detected (a strange noise, for example).
- Corrective: also called reactive or breakdown. It is the one that is execute when the failure has already occurred, and it is necessary to repair the damaged equipment.
- Predictive: it is a proactive maintenance method based on data designed to analyze the equipment’s state and continuously predict possible failures.
Features
Predictive maintenance allows maintenance frequency to be as low as possible. When care is schedule from time to time (preventive), two things can happen: either it is done when it is not necessary —early or late—incurring avoidable costs, or it is not done frequently enough, with the risk of equipment failure. Thus, the goal of predictive maintenance is to optimize the use of maintenance resources.
Advantages and disadvantages
Predictive maintenance ensures that a piece of equipment is only shut down before an imminent failure. This reduces operating costs, minimizes downtime and improves the overall performance of the machinery. However, the investment in the monitoring equipment required for this type of maintenance is usually high, as is the necessary knowledge and experience to interpret the data.
Predictive Maintenance Techniques
There are various techniques linked to predictive maintenance, and below, we review some of them:
Infrared Thermography
Worn parts and components, including electronic circuits, often produce more heat than average. Through infrared (IR) cameras, maintenance personnel can detect high temperatures (hot spots) on equipment.
Acoustic Monitoring
With acoustic sensors, maintenance personnel can detect equipment gas, liquid or vacuum leaks. Frictions and stresses in machines from worn or poorly lubricate bearings can also be detecte.
Vibration Analysis
It allows technicians to analyze the vibrations of a machine through sensors integrated into the equipment. A device that works in optimal conditions presents a particular vibration pattern, but when the components wear, the vibration frequencies change.
Examples
Many industries use predictive maintenance to save costs and improve the quality of their services. These are some examples:
Electrical Networks And Wind Turbines
Interruptions in electricity distribution systems are very costly. Hence, the advanced installation of intelligent networks allows knowing the necessary maintenance of the assets and thus anticipating breakdowns. The predictive is also apply to wind turbines to the detriment of the corrective to avoid their stoppage and the consequent potential loss of production.
Railway Lines
Railway networks and the trains that pass through them require constant maintenance. Using IoT, railway companies can identify problem areas in the network, optimize operating times and reduce the impact of breakdowns.
Marine Transport
Monitoring the status of a ship’s machinery allows remote diagnostics to be carry out from the offices on land to optimize maintenance operations and achieve the maximum performance of the boat.