Understanding models and applications is essential in modern technology, business, and scientific research. Whether in artificial intelligence, software development, education, or analytics, models provide structured ways to interpret data, while applications transform those models into practical solutions.
From machine learning algorithms powering recommendation systems to financial forecasting tools and educational simulations, models and applications shape decision-making across industries. This guide explains what they are, where they are used, their benefits, limitations, and how individuals and businesses can apply them effectively.
Table of Contents
Clear Definition of Models and Applications
A model is a simplified representation of a system, concept, or process used for analysis, prediction, or decision-making. Models may be mathematical, computational, conceptual, or statistical.
An application is the practical implementation of a model or system to solve real-world problems. Applications convert theoretical frameworks into usable tools, software, or operational solutions.
In simple terms:
-
Models help understand or predict outcomes.
-
Applications use those models to create functional solutions.
-
Together, they enable innovation across industries.
Who This Topic Is For
This guide is valuable for:
-
Students studying technology, AI, or data science
-
Business professionals exploring automation
-
Developers building predictive systems
-
Researchers analyzing complex datasets
-
Entrepreneurs leveraging digital tools
Anyone involved in technology-driven decision-making benefits from understanding models and applications.
Who Might Avoid Complex Model Implementation

Advanced modeling may not be suitable when:
-
Data availability is limited or unreliable
-
Technical expertise is lacking
-
Infrastructure investment is insufficient
-
Regulatory or ethical concerns restrict automation
In such cases, simpler approaches may be more practical.
Types of Models
Different disciplines use various types of models.
Conceptual Models
Used to represent ideas, workflows, or systems visually or logically. Common in education, business planning, and software design.
Mathematical Models
Used in finance, engineering, and physics to predict outcomes using equations and formulas.
Statistical Models
Used in data analysis to interpret patterns, trends, and probabilities.
Machine Learning Models
These learn from data and improve predictions over time. Examples include recommendation systems, fraud detection tools, and image recognition systems.
Simulation Models
Used in industries like aviation, healthcare, and manufacturing to test scenarios without real-world risks.
Each model type serves different purposes depending on complexity and industry needs.
Major Applications Across Industries
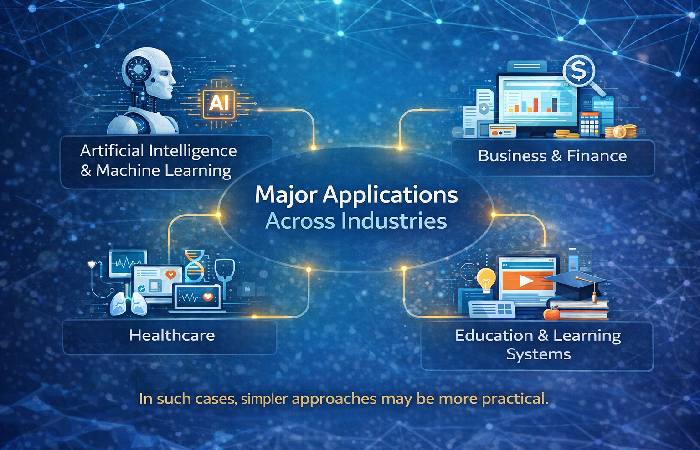
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI applications rely heavily on predictive models. Examples include:
-
Voice assistants and chatbots
-
Image recognition systems
-
Recommendation engines
-
Predictive analytics platforms
From experience working with AI-driven automation tools, these models significantly improve efficiency when paired with human oversight.
Business and Finance
Organizations use models for:
-
Financial forecasting
-
Customer behavior analysis
-
Risk management
-
Marketing optimization
Applications built on these models help companies make data-driven decisions.
Healthcare
Medical applications include:
-
Disease prediction models
-
Diagnostic imaging analysis
-
Personalized treatment planning
-
Drug discovery simulations
These applications enhance healthcare accuracy and efficiency.
Education and Learning Systems
Educational technology uses models for:
-
Personalized learning pathways
-
Adaptive testing systems
-
Performance analytics
-
Virtual tutoring platforms
These applications improve learning accessibility and outcomes.
Engineering and Manufacturing
Models help design products, optimize production, and predict equipment maintenance needs.
Applications based on these models improve safety, efficiency, and cost management.
Benefits of Models and Applications
Better Decision-Making
Models analyze data objectively, helping reduce guesswork.
Efficiency Improvements
Automation powered by models reduces repetitive tasks.
Innovation Support
Advanced modeling enables new products, services, and discoveries.
Cost Optimization
Predictive applications help prevent errors and reduce operational expenses.
Scalability
Applications based on models can grow alongside business needs.
These benefits explain why modeling is central to modern technology strategies.
Drawbacks and Challenges
Despite advantages, challenges exist.
Data Quality Issues
Poor data leads to inaccurate models.
Complexity
Advanced models require specialized skills.
Implementation Costs
Infrastructure and expertise investment can be significant.
Ethical Concerns
Bias, privacy, and transparency issues must be addressed.
Overreliance on Automation
Human oversight remains essential.
Recognizing these challenges helps responsible adoption.
Common Mistakes When Using Models
Typical errors include:
-
Ignoring data quality requirements
-
Overcomplicating simple problems
-
Failing to validate models regularly
-
Misinterpreting outputs
-
Neglecting ethical implications
Avoiding these mistakes improves reliability.
Myths vs Facts
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| Models always produce accurate predictions | Accuracy depends on data and assumptions |
| Applications eliminate human involvement | Human oversight remains crucial |
| Modeling is only for scientists | Businesses widely use modeling tools |
| More complex models are always better | Simpler models can be more effective |
Understanding these realities prevents unrealistic expectations.
Practical Tips for Effective Implementation

Start with Clear Objectives
Define what problem the model should solve.
Focus on Data Quality
Clean, relevant data improves accuracy.
Test Continuously
Regular validation prevents performance decline.
Maintain Transparency
Explainable models build trust.
Combine Human Expertise
Human insight enhances automated outputs.
From practical experience, organizations achieve the best results when models complement human decision-making rather than replacing it.
Real-World Example
A retail company might use a predictive sales model:
-
Historical sales data is analyzed.
-
Seasonal trends are identified.
-
Demand forecasts are generated.
The application built on this model helps optimize inventory, reduce waste, and improve profitability.
This demonstrates how theoretical modeling translates into practical business value.
Future Trends in Models and Applications
Technology continues evolving rapidly.
Key trends include:
-
Generative AI models transforming creativity
-
Edge computing applications for real-time processing
-
Automated decision systems in industries
-
Increased ethical AI regulations
-
Integration with Internet of Things devices
These developments will expand model-based applications significantly.
FAQs About Models and Applications
What are models in technology?
Models are structured representations used to analyze data, predict outcomes, or simulate processes.
What are applications?
Applications implement models to solve practical problems.
Where are models commonly used?
Artificial intelligence, finance, healthcare, education, engineering, and business analytics.
Are models always accurate?
Accuracy depends on data quality, assumptions, and continuous validation.
Why are applications important?
They turn theoretical insights into actionable solutions.
Also Read:
Use existing live pages on your website for:
Avoid linking to non-existent pages to prevent SEO issues.
Final Conclusion
Understanding models and applications is crucial in today’s technology-driven world. Models provide structured ways to interpret data and predict outcomes, while applications bring those insights into practical use. From artificial intelligence to healthcare, finance, and business automation, these tools drive innovation, efficiency, and smarter decision-making. When implemented responsibly with high-quality data and human oversight, models and applications become powerful assets for individuals and organizations alike.
High-Authority Sources Used
-
https://www.oecd.org/en/topics/policy-issues/artificial-intelligence.html
-
https://www.britannica.com/technology/artificial-intelligence
These sources provide authoritative insights into modeling concepts, artificial intelligence applications, and real-world technology implementations.