We have already seen in some other blog entries the main dangers to which we are subject when browsing the Internet. One of the main ones is Phishing, which is one of the most used methods by cybercriminals to scam and fraudulently obtain confidential information, such as bank information or a password. The attack is usually carry out using an email, which appears to come from trusted sources (such as a bank). In reality, it seeks to manipulate the recipient to steal confidential information.
We are going to list a series of indicators that use to identify a fake email. None of them is infallible or definitive, but they can help protect us from fraudulent emails or Phishing.
Table of Contents
Telecommunications Companies
Companies (banks, telecommunications companies.) rarely ask us for personal data through email. The mere reception of these emails makes us suspicious, and we must be on our guard.
Basic Verification
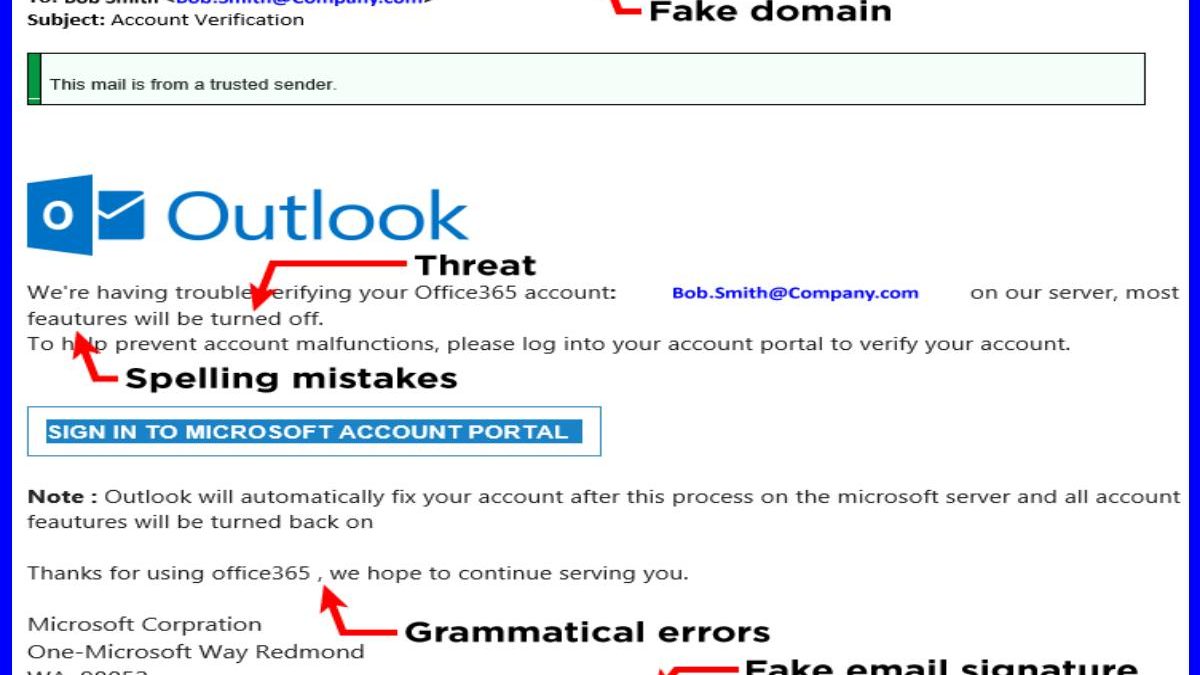
The most basic verification that is complete is that the email domain (what comes after the @ symbol) agrees with the company that is theoretically sending the email. It must be a sphere that leaves no room for doubt that it is legitimate. Sometimes scammers make fakes that can make you doubt. For example, an email supposedly sent by PayPal is notice@ppal.com, where ppal.com could sound like it is part of PayPal, but it is not.
Being Messages Sent to Many Recipients
The mail is not modified with the recipient’s name, so its greeting is similar to “Dear customer”. A legitimate company or organization will almost always send emails addressed to you.
These emails usually deal with
billing problems, requests from the authorities, bank alerts, prize communications, urgent business opportunities…
Attachments
if a company or association sends you a document, the format will typically be a PDF. Special care should be taken with images. As a rule of thumb, if the file is in HTML, EXE, or some other format that causes the operating system to ask for your permission to run it, it’s almost certainly malware or Phishing.
Phishers or Cyber Criminals
Phishers or cyber criminals like to play with urgency, and this type of email will write in such a method that it gives you a sense of urgency to click on any of the links or images they offer. They will use phrases like “your account needs to be updated”, “your account is about to erase”, and “doubtful activity a sense in your account”…. You must not believe the threats, and you must try to remain calm. No legitimate entity, neither governmental nor business, nor of any kind, will give you a single and urgent possibility to respond or do what is required.
Addresses are Misleading,
Some addresses are misleading, so before clicking on a link, it is convenient to move the mouse over it (without clicking). This causes almost all email clients to display the address or URL of the web page to which the link goes. If this address does not agree to the company or organization that supposedly sends the mail, it is a fraud.
URL of the Page
If you ask to provide sensitive information, check that the URL of the page you are linking to starts with “HTTPS” instead of just “HTTP”. The “S” stands for “safe.” It is not a guarantee that a site is legitimate, but most legitimate sites use HTTPS because it is more secure. HTTP sites, even legitimate ones, are vulnerable to hackers. Specific web pages often display a closed padlock symbol in the address bar for added security.
Wrong Account
suppose you have several email accounts, and the email has reached an address you have not provided to the company or organization that supposedly sends you the email. In that case, you can suspect it is a fraud attempt.
Therefore, and as an essential precautionary measure, do not hesitate to send it directly to the spam folder if you have received an email you have any suspicion about. Your email client (Gmail, Outlook, …) will separate all future emails that the sender of the said message may send you and delete them after a while.
Although this type of email phishing is the most common, there are also other types :
Website Phishing
These are fake copies of websites you know and trust. Hackers create these sites to trick users into entering their login credentials and connecting to their accounts, and it can also do through popup windows.
Vishing or Voice Phishing
The attacker tries to convince victims over the phone to provide them with the information they can use to impersonate them.
Smishing – This is SMS Phishing
The victim receives a text note asking them to click on a link or download an app. Doing so can download malware to your mobile phone that can capture your personal information.
Phishing Through Social Networks
Through the creation of false profiles, they try to deceive their victims.
By following these instructions and being a little cautious, we hope we can prevent cybercriminals from getting away with it and that they do not manage to impersonate our identity and steal our data. If this is not possible, I hope we make it more and more difficult for them so that we can finally end this type of criminal practice over time.